📌 Introduction
A Forward Proxy is a critical component in network security and privacy. It acts on behalf of clients to access the internet while hiding their identity. It helps ensure anonymity, access control, and traffic monitoring. This guide will cover everything you need to know about Forward Proxies, from the basics to real-world use cases.
⚙️ What is a Forward Proxy?
A Forward Proxy is a server that sits between a client (such as a user or device) and the internet. It intercepts outbound requests from the client, evaluates or modifies them, and forwards them to the destination server. The external server never sees the original client’s IP address, only that of the proxy.
🧩 Key Benefits
- Privacy: Masks user identity by hiding the original IP address.
- Access Control: Restricts user access to specific websites or services.
- Traffic Filtering: Blocks malicious or inappropriate content at the gateway.
- Bandwidth Savings: Caches frequently accessed content for faster delivery.
🔧 Types of Forward Proxies
- Anonymous Proxy: Hides the client’s identity but reveals it is using a proxy.
- Transparent Proxy: Intercepts traffic without modifying requests or revealing itself.
- High Anonymity Proxy: Hides the fact that a proxy is being used and masks the client IP completely.
- SOCKS Proxy: Works at a lower level and supports various protocols, including TCP and UDP.
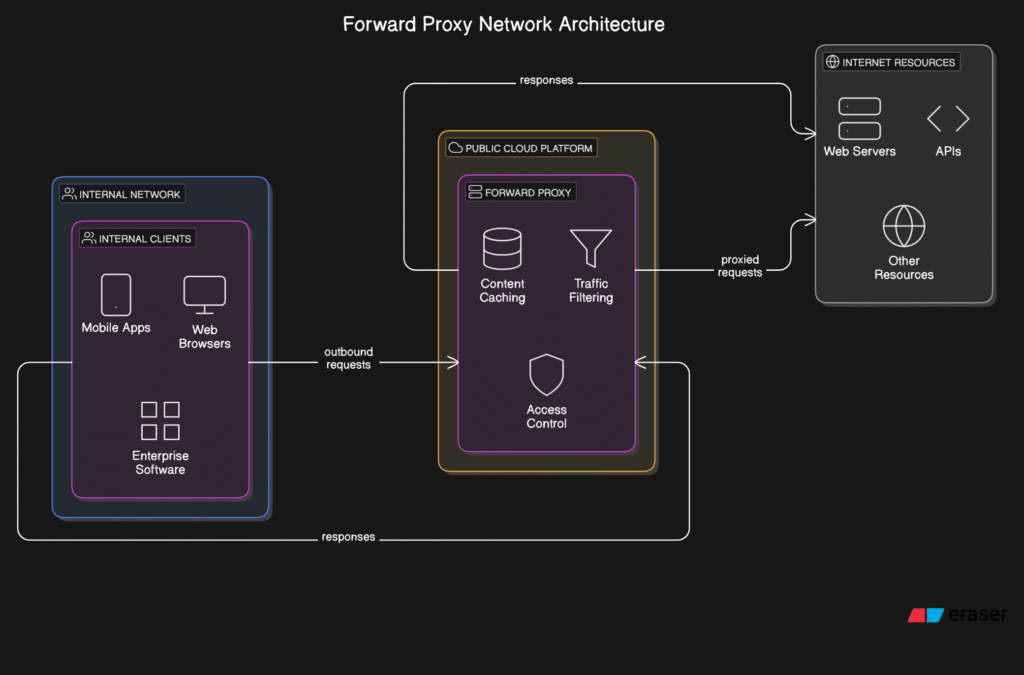
This Forward Proxy Network Architecture shows how internal clients (like mobile apps, browsers, and enterprise software) send outbound internet requests through a forward proxy. The proxy, hosted on a cloud platform, handles:
- Content caching
- Traffic filtering
- Access control
It forwards (proxies) the requests to internet resources (like web servers and APIs), then returns the responses back to the internal clients—providing security, control, and optimization for internet access.
🔁 Use Cases
- Corporate Networks: Monitor and restrict employee internet usage.
- Content Filtering: Block access to harmful or non-compliant sites.
- Geo-Bypassing: Access content not available in the user’s region.
- Security Monitoring: Log outgoing traffic to detect anomalies.
⚙️ Tools & Services
- Open-Source Tools:
- Squid: A powerful caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy.
- Privoxy: A privacy-focused filtering proxy for web browsers.
- Cloud-Native Solutions:
- Zscaler: Cloud-based proxy offering secure internet access for enterprises.
- FortiProxy: Enterprise-grade forward proxy with traffic filtering and security.
✅ Best Practices
- Implement Logging: Keep track of outgoing requests for auditing and debugging.
- Use Access Control Lists (ACLs): Define rules to manage who can access what.
- Enable Caching: Reduce load and improve speed by caching repeated content.
- Encrypt Communication: Use HTTPS between client and proxy for secure transmissions.
🔐 Security Implications
- Data Leakage Risk: Misconfigurations can lead to exposure of sensitive user data.
- Abuse by Malicious Users: Can be used to hide identity for malicious activities if left open.
📚 Real-World Examples
- Schools and Universities: Use proxies to restrict content access and monitor internet usage.
- Corporate IT: Enforce internet usage policies and enhance outbound traffic security.
- VPN Services: Some VPNs internally use forward proxies to reroute user traffic.
🚀 Conclusion
Forward Proxies are a vital component in network privacy, access control, and traffic monitoring. Whether you’re securing a corporate network, enforcing usage policies, or enhancing user anonymity, forward proxies offer robust capabilities to control and filter outgoing internet traffic.
3 FAQs About Forward Proxy
- What is the primary function of a Forward Proxy?
To act on behalf of clients, forwarding their requests to external servers and masking their identity. - How does a Forward Proxy differ from a Reverse Proxy?
A forward proxy serves client-side traffic, while a reverse proxy handles traffic directed at backend servers. - Are Forward Proxies secure?
They can be, but require proper configuration to avoid data leaks and misuse.

